What is Google PageRank? Detailed Explanation of Google PageRank
When it comes to SEO (Search Engine Optimization), one term you cannot overlook is Google PageRank. Although Google no longer publicly updates this metric, its influence and fundamental concepts remain significant in understanding how Google ranks websites. In this article, we will explore what Google PageRank is, how it works, and why it still matters in today’s SEO landscape.
What is Google PageRank?
Google PageRank (often abbreviated as PR) is an algorithm developed by Google founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin in 1996 while they were Ph.D. students at Stanford University. The name “PageRank” is derived from Larry Page’s surname and refers to a system that evaluates the importance of web pages.

What is Google PageRank?
In simple terms, PageRank measures the quality and quantity of links pointing to a website to determine its authority and relevance. The more high-quality and relevant backlinks a page has, the higher its PageRank score is likely to be. This score ranges from 0 to 10, with 10 being the highest.
How Does Google PageRank Work?
PageRank operates on the principle that not all links are equal. A link from a reputable, authoritative website (e.g., BBC, Wikipedia) carries more weight than a link from a low-quality or obscure site. Here’s a breakdown of how it functions:
- Link Analysis: PageRank assesses the number of inbound links to a page. However, quantity alone isn’t enough—it also evaluates the quality of those links.
- Weight Distribution: Each link “votes” for the page it points to, passing a portion of its own PageRank value. The value transferred depends on the linking page’s authority and the number of outbound links it has.
- Damping Factor: To prevent manipulation and infinite loops, Google applies a damping factor (typically set at 0.85). This means only 85% of a page’s PageRank is distributed to linked pages, while the remaining 15% is “lost” or retained by Google’s algorithm.
- Iterative Calculation: PageRank is calculated iteratively across the web. The process repeats until the scores stabilize, providing a final value for each page.
In essence, PageRank simulates how a user might randomly navigate the web, clicking links and moving between pages, with the algorithm assigning importance based on this behavior.
How Does Google PageRank Work?
The History of Google PageRank
- 1996: Larry Page and Sergey Brin began developing PageRank as part of their research at Stanford.
- 1998: PageRank became the foundation of Google’s search engine, distinguishing it from competitors like Yahoo and AltaVista.
- 2000: Google introduced the PageRank Toolbar, allowing users to see the PageRank score (0–10) of any webpage. This became a key metric for SEO professionals.
- 2013: Google stopped updating the public PageRank Toolbar, signaling a shift away from sharing this data.
- 2016: Google officially discontinued the Toolbar PageRank, though the algorithm (or an evolved version) remains part of its ranking system.
Does Google PageRank Still Matter Today?
Although Google no longer displays PageRank scores publicly, the underlying concept of link-based authority remains integral to its ranking algorithm. Modern SEO has evolved beyond just PageRank to include hundreds of other factors, such as content quality, user experience, mobile-friendliness, and site speed. However, backlinks—especially from authoritative sources—are still a critical ranking signal.
You can check the PageRank score through several tools.
Here’s why PageRank concepts are still relevant:
- Link Quality Over Quantity: Google prioritizes high-quality, relevant links over spammy or low-value ones, a principle rooted in PageRank.
- Authority and Trust: Websites with strong domain authority (a modern metric inspired by PageRank) tend to rank higher.
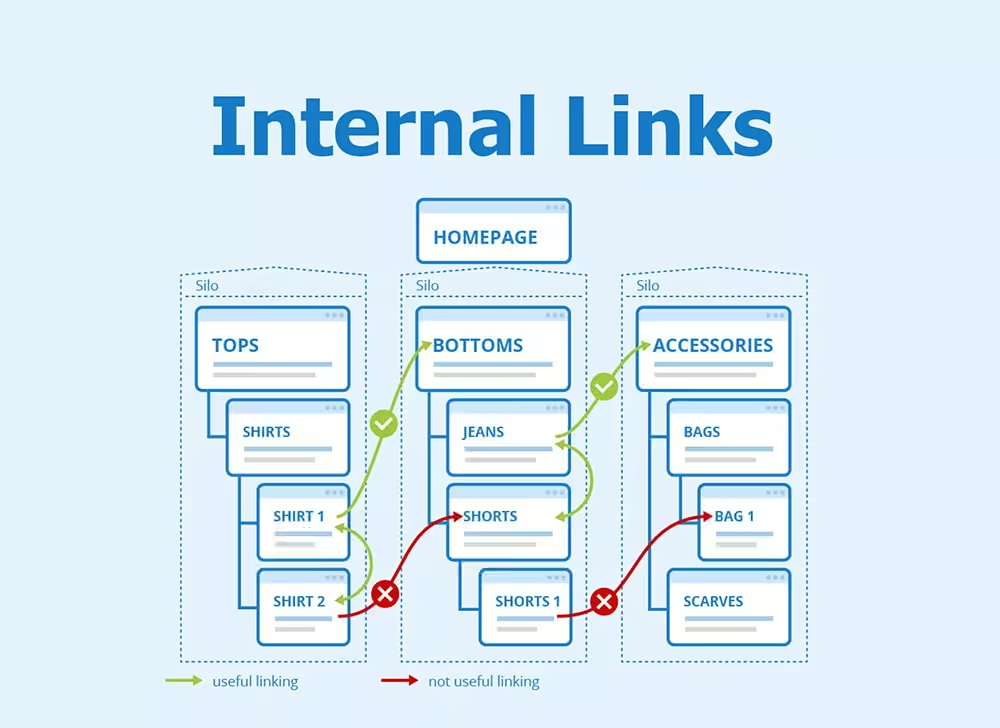
- Internal Linking: PageRank also applies to how link equity is distributed within a website, making internal linking strategies vital.
How to Improve Your Website’s “PageRank”?
Since PageRank is no longer a visible metric, SEO efforts now focus on boosting overall site authority. Here are some actionable tips:
- Build High-Quality Backlinks: Earn links from reputable websites in your niche through guest posting, partnerships, or creating valuable content.
- Optimize Internal Linking: Ensure important pages receive more internal links to distribute link equity effectively.
- Create Valuable Content: High-quality, original content naturally attracts backlinks and improves your site’s authority.
- Avoid Black-Hat Tactics: Spammy link-building practices (e.g., buying links) can lead to penalties from Google.
- Monitor Your Competitors: Analyze their backlink profiles to identify opportunities for your own site.
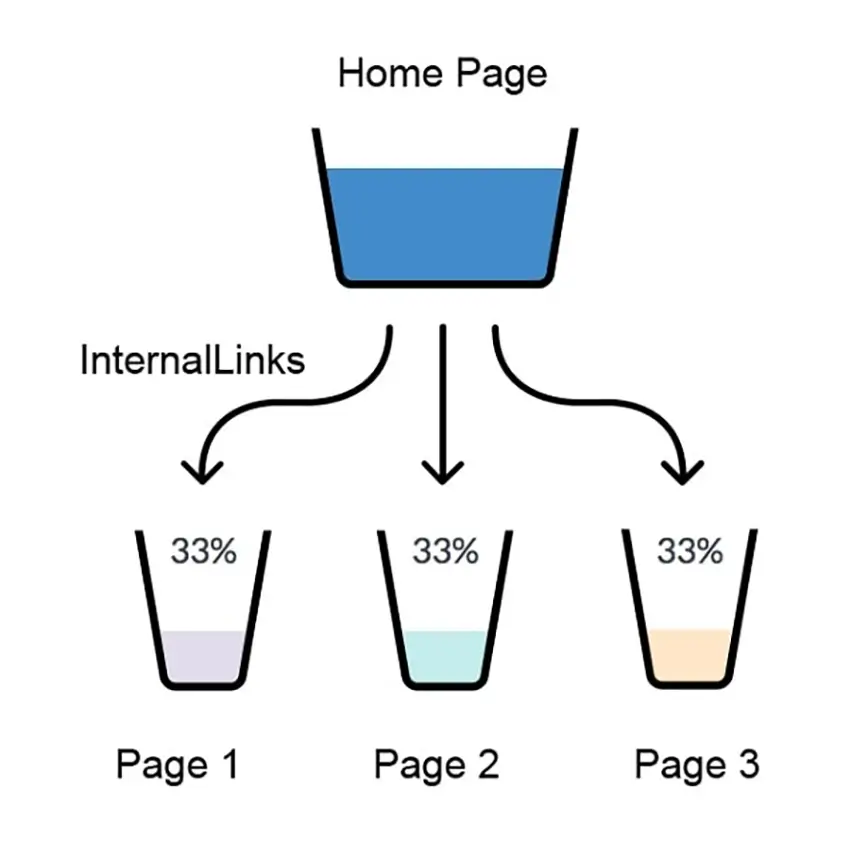
Reasonably distributing internal links helps optimize PageRank.
Conclusion
Google PageRank may no longer be a public metric, but its legacy lives on in how Google evaluates websites. Understanding its principles—particularly the importance of quality links—can help you refine your SEO strategy and improve your site’s ranking on search engine results pages (SERPs). In 2023 and beyond, focusing on authority, relevance, and user value remains the key to success in the ever-evolving world of SEO.
For more SEO insights and strategies, don’t forget to follow Leadigital!
- Office: 215 Nguyen Gia Tri, Ward 25, Binh Thanh District, HCMC
- Hotline: 093 2323 799
- Website: https://leadigital.vn/
- Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/leadigital.vn